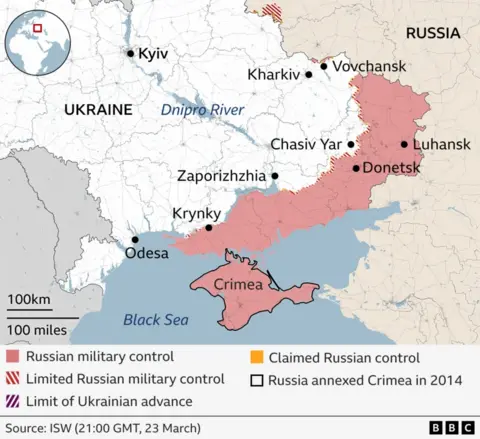
Russia and Ukraine have agreed to a naval ceasefire in the Black Sea in separate deals with the US, after three days of peace talks in Saudi Arabia.
Washington said all parties would continue working toward a “durable and lasting peace” in statements announcing the agreements, which would reopen an important trade route.
They have also committed to “develop measures” to implement a previously agreed ban on attacking each other’s energy infrastructure, the White House said.
But Russia said the naval ceasefire with Ukraine would only come into force after a number of sanctions against its food and fertiliser trade were lifted.
US officials have been separately meeting negotiators from Moscow and Kyiv in Riyadh with the aim of brokering a truce between the two sides. The Russian and Ukrainian delegations have not met directly.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky said the deal to halt strikes in the Black Sea was a step in the right direction.
“It is too early to say that it will work, but these were the right meetings, the right decisions, the right steps,” he told a press conference in Kyiv.
“No-one can accuse Ukraine of not moving towards sustainable peace after this,” he added, after US President Donald Trump had previously accused him of blocking a peace deal.
But shortly after Washington’s announcement, the Kremlin said the Black Sea naval ceasefire between Russia and Ukraine would not take effect until sanctions were lifted from Russian banks, producers and exporters involved in the international food and fertiliser trades.
The measures demanded by Russia include reconnecting the banks concerned to the SwiftPay payment system, lifting restrictions on servicing ships under the Russian flag involved in the food trade, and on the supply of agricultural machinery and other goods needed for the production of food.
It was unclear from the White House’s statement when the agreement is meant to come into force.
When asked about lifting the sanctions, Trump told reporters: “We’re thinking about all of them right now. We’re looking at them.”
Washington’s statement on the US-Russia talks does say the US will “help restore Russia’s access to the world market for agricultural and fertiliser exports”.
Speaking in Kyiv, Zelensky described this as a “weakening of positions”.
He also said Ukraine would push for further sanctions on Russia and more military support from the US if Moscow reneged on its commitments.
Later, in his nightly address to Ukrainians, Zelensky accused the Kremlin of lying when it said the Black Sea ceasefire depended on sanctions being lifted.
Ukraine’s Defence Minister Rustem Umerov said “third countries” could oversee parts of the deal.
But he warned that the movement of Russian warships beyond the “eastern part of the Black Sea” would be treated as a violation of the agreement and a “threat to the national security of Ukraine”.
“In this case Ukraine will have full right to exercise right to self-defence,” he added.
Also See: US Officials To Hold Separate Meetings With Russia, Ukraine in Saudi Arabia on Monday
A previous arrangement allowing safe passage of commercial ships in the Black Sea was agreed in 2022, after Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February of that year.
Both Ukraine and Russia are major grain exporters, and prices rocketed after the start of the war.
The “Black Sea grain deal” was put in place to allow cargo ships travelling to and from Ukraine to safely navigate without being attacked by Russia.
The deal facilitated the movement of grain, sunflower oil and other products required for food production, such as fertiliser, through the Black Sea.
It was initially in place for a period of 120 days but, after multiple extensions, Russia pulled out in July 2023, claiming key parts of the agreement had not been implemented.
After this week’s talks, both countries have also agreed to “develop measures” to implement a ban on attacking energy infrastructure on each other’s territory.
Russian strikes on Ukraine’s power supply have caused widespread blackouts throughout the war, leaving thousands of people without heating in the cold of winter.
Attacks on Ukraine’s nuclear power stations have led the UN’s atomic watchdog to call for restraint.
A ban was initially agreed in a call between Trump and his Russian counterpart Vladimir Putin last week, but within hours of it being announced, both Moscow and Kyiv accused the other of breaching it.
Earlier on Tuesday, Moscow said Ukraine had continued to target Russia’s civilian energy infrastructure while the peace talks in Riyadh were under way.
The alleged attack showed Zelensky was “incapable of sticking to agreements”, Russia’s defence ministry said.
It came after Russia launched a missile strike targeting north-eastern Ukraine on Monday, leaving more than 100 people wounded in the city of Sumy.
On Tuesday morning, Ukraine said Russia launched some 139 drones and one ballistic missile overnight.
Up to 30 Russian troops were killed in an air strike on military infrastructure in Kursk, Kyiv added.
This news is sourced from BBC and is intended for informational purposes only.

![Russia and Ukraine agree to a naval ceasefire in the Black Sea, but Russia links its enforcement to sanctions relief. [Image via Getty Images/File]](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/76e6b930-09b8-11f0-94d4-6f954f5dcfa3.jpg.webp)
![Ukrainian and Russian flags with soldier silhouettes representing ongoing conflict. [Image via Atlantic Council].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/2022-02-09T000000Z_1319661209_MT1NURPHO000HXCNME_RTRMADP_3_UKRAINE-CONFLICT-STOCK-PICTURES-scaled-e1661353077377.jpg)


![Truck traveling along the Makran Coastal Highway in Balochistan, with rugged cliffs and the Arabian Sea coastline in the background [Image via Getty Images].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Balochistan-2.webp)