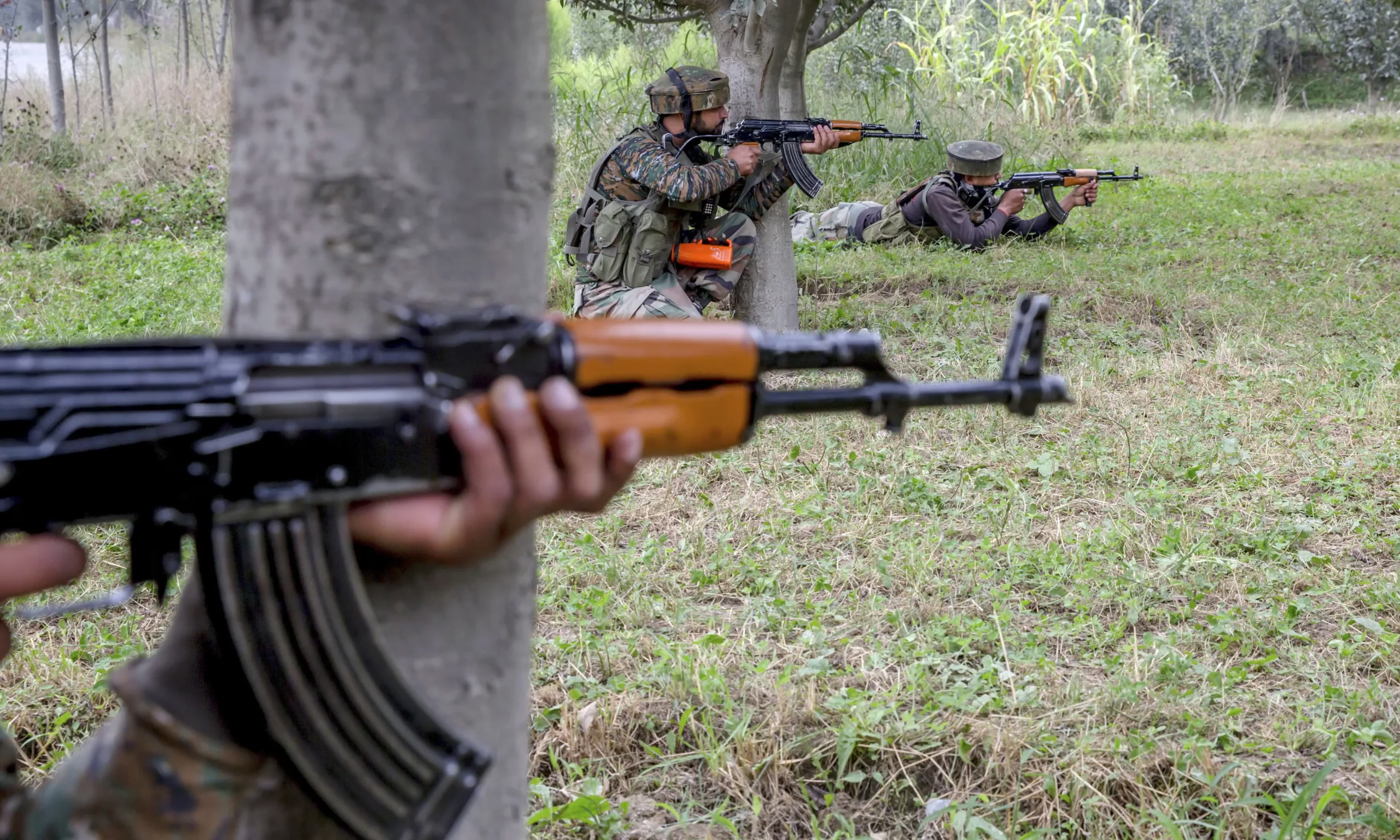
Narcotics trafficking in South Asia, particularly in the Golden Crescent, has brought devastating consequences to the region. Pakistan has suffered the brunt of these effects. The illicit drug trade not only finances terrorism and organized crime but also severely hinders economic development.
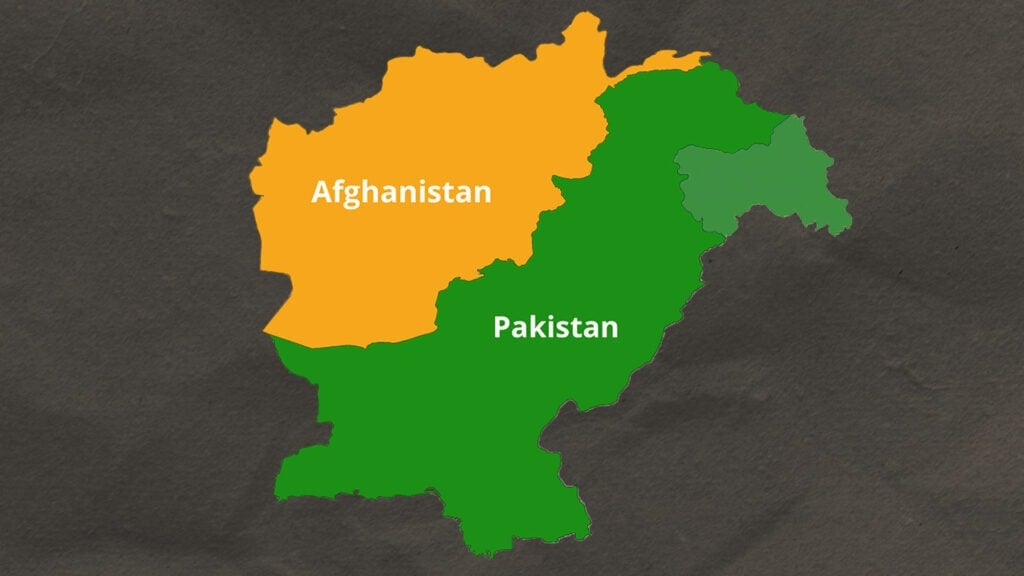
Drug trafficking between Pakistan and Afghanistan began in the 1970s and 1980s when Afghanistan became a significant opium-producing region. The Soviet invasion in 1979 exacerbated the situation, leading to the proliferation of drug trafficking routes. The porous 2,640-kilometer-long border between Pakistan and Afghanistan, with its rugged terrain and limited control, became a critical conduit for narcotics. The chaos of war, combined with the rise of the Mujahideen and later the Taliban, entrenched the drug trade in the region.
The Golden Crescent: A Hub of Narcotics Trafficking
The world has long recognized the Golden Crescent—comprising Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan—as a major hub for producing and trafficking narcotics, particularly opium and heroin. Afghanistan is at the center of this trade and is the world’s largest producer of opium. In 2022 alone, Afghanistan produced an estimated 6,400 tons of opium.
Taliban’s resurgence in 2021 reinvigorated the opium trade. Despite the Taliban’s 2022 poppy cultivation ban, Afghanistan remains the world’s largest producer of opiates. Significant quantities of these opiates are smuggled into Pakistan. The porous border, coupled with the challenges of securing such a vast expanse, continues to facilitate the illicit drug trade. This staggering volume fuels addiction and generates billions of dollars in illegal revenue. Much of this revenue finds its way into Pakistan, funding a wide array of criminal activities.
The Economic and Social Cost of Drug Money
The economic toll of drug trafficking in Pakistan is staggering. The 2024 National Drug Survey, scheduled for completion this year, follows a 2012-13 survey revealing that 6.7 million Pakistanis used drugs other than alcohol and tobacco in the previous year. Drug money’s influence extends beyond economics. It fuels organized crime and terrorism, creating a cycle of violence and instability. According to a 2021 UNODC report, numerous militant groups in Pakistan rely on narcotics trafficking as a primary income source. This relationship between drug traffickers and terror organizations undermines national security, as drug revenues fund operations that destabilize the region and challenge state sovereignty.
According to a World Bank report, Pakistan ranks third in the world in water scarcity, a crisis exacerbated by the diversion of resources towards combating the drug trade. The funds that could have been allocated to critical infrastructure projects, healthcare, and education are instead funneled into anti-narcotics operations and security measures. The illicit drug trade also contributes to a parallel economy that operates outside the legal framework, undermining the formal economy. The global narcotics trade generates between $426 and $652 billion annually, according to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). Criminals launder a significant portion of this through legal businesses, further distorting economic data and tax revenues in Pakistan.
Escalating Drug Abuse Among Youth
The social fabric of Pakistan is being torn apart by the narcotics trade. The country’s youth, who make up a significant portion of the population, are particularly vulnerable. The resurgence of Pakistan’s National Drug Survey after an 11-year hiatus revealed a critical national security threat posed by unchecked drug abuse. The survey highlighted the intricate link between narcotics, terrorism financing, and organized crime, with a focus on the impact on youth, particularly in educational institutions.
In Karachi, Islamabad, and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, drug addiction is rampant, leading to a surge in crime rates. Educational institutions, once considered safe havens for learning, have become recruitment grounds for drug traffickers and extremist groups.
The impact of drug trafficking on Pakistan’s youth is particularly alarming. A 2023 study found that nearly 25% of college students in Pakistan have experimented with drugs. The infiltration of drugs into schools and universities is not just a public health issue; it is a direct threat to the nation’s future. The impact of narcotics on public health is also severe. The rise in drug-related diseases, including HIV/AIDS and hepatitis, places an additional burden on the already strained healthcare system. The cost of treating these diseases, coupled with the loss of productivity due to addiction, creates a vicious cycle that further entrenches poverty and underdevelopment.
The Link Between Narcotics and Terrorism
The economic implications of drug trafficking are intricately linked to terrorism. In Pakistan, drug money is a critical resource for extremist groups, including the Tehreek-i-Taliban Pakistan (TTP). The TTP has long used drug profits to finance their insurgency, further destabilizing regions like Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, which borders Afghanistan. This region’s porous borders facilitate the easy flow of drugs, exacerbating both local and national security concerns.
In cities like Karachi, the situation is equally dire. The city’s sprawling slums have become epicenters of drug trafficking, with heroin, crystal meth, and synthetic drugs flooding the market. The revenue generated from these illegal activities supports extremist groups that use Karachi as a base for recruitment and operations. This connection between drug trafficking and terrorism not only fuels violence but also hampers development efforts in one of Pakistan’s largest economic hubs.
The Triangular Initiative’s Efforts
The Triangular Initiative, facilitated by the UNODC and involving Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan, has made some strides in addressing the narcotics trade. The establishment of Border Liaison Offices (BLOs), the enhancement of regional response through information-sharing, and the planning of simultaneous patrolling operations are steps in the right direction.
Conclusion
To effectively combat the narcotics trade and its associated economic toll, Pakistan must take a multi-faceted approach. Strengthening regional cooperation through initiatives like the Triangular Initiative is crucial. Moreover, Pakistan must invest in its anti-narcotics infrastructure, including better training for law enforcement agencies, enhanced border security, and comprehensive rehabilitation programs for addicts. The economic development of border regions, particularly in Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, should be prioritized to provide alternative livelihoods to those involved in the drug trade.
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own. They do not necessarily reflect the editorial policy of the South Asia Times.

![The Golden Crescent's narcotics trafficking harms Pakistan, fueling terrorism, stalling economic growth, and eroding country's social fabric [Image via Pixabay].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/684307_0_98_1920_1178_1920x0_80_0_0_8b578c90206789cceadb994a04c397ff.webp)


![Ukrainian and Russian flags with soldier silhouettes representing ongoing conflict. [Image via Atlantic Council].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/2022-02-09T000000Z_1319661209_MT1NURPHO000HXCNME_RTRMADP_3_UKRAINE-CONFLICT-STOCK-PICTURES-scaled-e1661353077377.jpg)