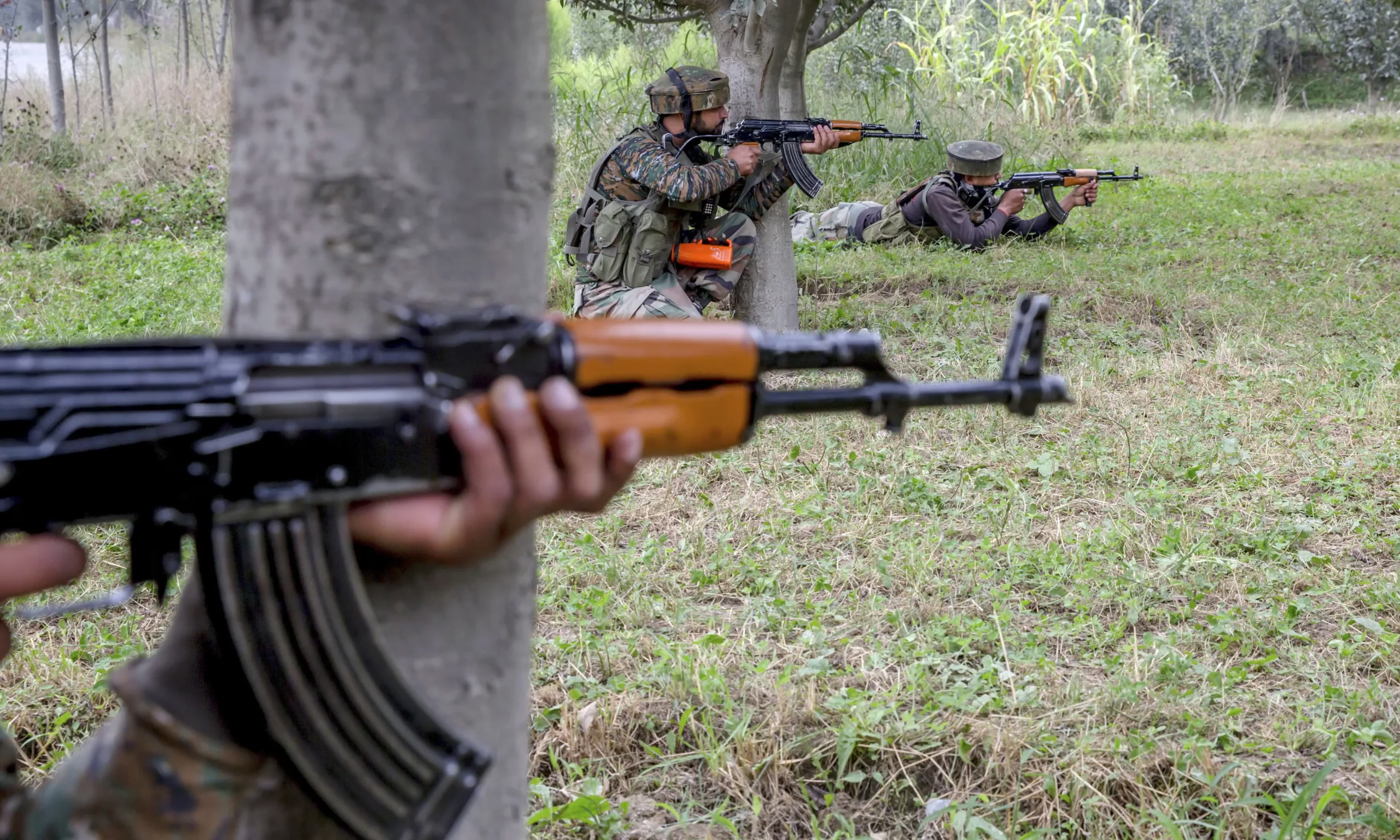
Recently, the visit of the United States Deputy Secretary of State Ms. Wendy Ruth Sherman to South Asia has been the center of discussion in the regional and international media. Along with the mutual areas of interest and the bilateral relations, the dominant discourse mainly revolved around Taliban-led Afghanistan.
The reason that Washington has long been managing the diplomatic maneuvering through the generals and intelligence agencies, therefore Ms. Sherman’s visit can be viewed in terms of a revival of the United States civilian diplomatic outreach in response to the changing dynamics of regional and global security paradigm in the wake of the US troop withdrawal from Afghanistan.
As Ronan Farrow states in the prologue of War on Peace – The Decline of American Influence, “Around the world, from Mogadishu to Damascus to Islamabad, uniformed officers increasingly handled the negotiations, economic reconstruction, and infrastructure development for which the United States once relied on a devoted body of trained specialists”.
Also Read: Afghanistan Endgame or a Beginning of a New Game?
The post 9/11 shift in the US foreign policy when the tools of American diplomacy were confined to military diplomacy – the diplomatic structures suffered a decline to deal with the complex set of challenges ranging from Islamophobia, cyberterrorism, rising Russian authoritarianism, revisionist China, and Afghan scenario to regional geopolitics. Therefore, the recent visit of the United States Secretary of State Ms. Wendy Ruth Sherman starting from Geneva, Switzerland on September 29th – to lead a US interagency delegation to a September 30th US-Russia bilateral Strategic Stability Dialogue, and to inaugurate the first US-Swiss Strategic Partnership Dialogue with Swiss State Secretary Livia Leu in Bern – ending in Pakistan on 7-8th October, visiting Uzbekistan and India, becomes significant as it comes at a time when in some way world’s center of gravity is being defined by the Silk Roads connecting Asia and Europe.
Hence, the visit starting from Europe and ending in Asia can be argued in terms of the emerging Eurasian trends – Is this indicative of the Biden administration’s Foreign policy being shaped in the Eurasian context?
Against this backdrop, it is indeed challenging for the Biden administration to rebuild and reinvent America’s diplomatic enterprise in the age of multipolar rivalries where power structures are diffused into diversified ideological, and political visions. Moreover, the reputation of the United States in recent years to walk the talk in the international setting to showcase the benefits of the alliances when it comes to collaboration, such as, over the War on Terror in Afghanistan – the US lags far behind in this exceedingly competitive field.
Pakistan, a case in point – from America’s most allied ally to the most sanctioned ally, and now Biden administration’s Pakistan policy – Here it is notable that Pakistan’s Premier Imran Khan’s statement regarding Pakistan’s Government negotiation with some of the factions of Tehreek-i-Taliban Pakistan (TTP), and Ms. Wendy Sherman’s statement seeking Pakistan’s “strong partnership on counterterrorism expecting sustained action against all militant and terrorist groups without distinction”, both appear on the same day. Besides, her visit to the Western Naval Command Mumbai, India; the western seaboard, fundamental for the sea conflicts against Pakistan, in addition to her views on Pakistan expressed in India followed by her statements in Pakistan – what should it be considered? A strategic panic or a strategic maneuver to test the waters?
Characterized by the themes of multipolarity, regional connectivity, and geoeconomics, South Asia, today, is home to the states coping with ethnonational and ethnoreligious fault-lines, and territorial conflicts in addition to the climate crisis, so does Central Asia.
At the same time, the changing dynamics of the security paradigm from conventional to non-conventional in the wake of the transition in Afghanistan has introduced a great power rivalry in which both the regional and international players are jostling for the central stage.
Just like every ending is a new beginning, the end of the twenty-year US-led Afghan War has contributed to the beginning of a strategic revolution that is pivoted to Eurasia and is taking place gradually yet surely!

![Sherman from United States met with Pakistan's Foreign Minister Qureshi in Islamabad [Image by Pakistan Ministry of Foreign Affairs via AP].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/AP21281255820748.webp)

![Ukrainian and Russian flags with soldier silhouettes representing ongoing conflict. [Image via Atlantic Council].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/2022-02-09T000000Z_1319661209_MT1NURPHO000HXCNME_RTRMADP_3_UKRAINE-CONFLICT-STOCK-PICTURES-scaled-e1661353077377.jpg)