In the three months since becoming Bangladesh’s interim leader following a student-led revolution, Muhammad Yunus has endured political turmoil, impatient cries for elections, and destructive flooding across the low-lying nation, while now also having to navigate the complex landscape of climate finance.
Now, the Nobel Peace Prize winner has been thrust into a brawl over money to help poorer countries deal with climate change—and he is not pleased about it.
The 84-year-old micro-finance pioneer, who took over after the toppling of autocratic leader Sheikh Hasina in August, likened the haggling at the UN COP29 climate finance summit to a “fish market”.
“I think that’s very humiliating, for nations to come and ask for money to fix…[the] problem that others caused for them,” Yunus told AFP in an interview in Azerbaijan, which is hosting the talks.
“Why should we be dragged here to negotiate? You know the problem.”
Nations hope to land a deal at COP29 that boosts funding for climate action in developing nations like Bangladesh, which are least responsible for global warming, but most at its mercy.
Some want $1 trillion a year to cover the enormous cost of shifting their economies to clean energy, and adapting to ever-more erratic and extreme weather.
But rich countries—whose rise to prosperity and associated carbon emissions have driven global warming—are reluctant to commit such large sums and want others to chip in.
The talks have hit a wall, frustrating leaders of climate-imperilled nations who left behind populations in dire straits to travel to Baku.
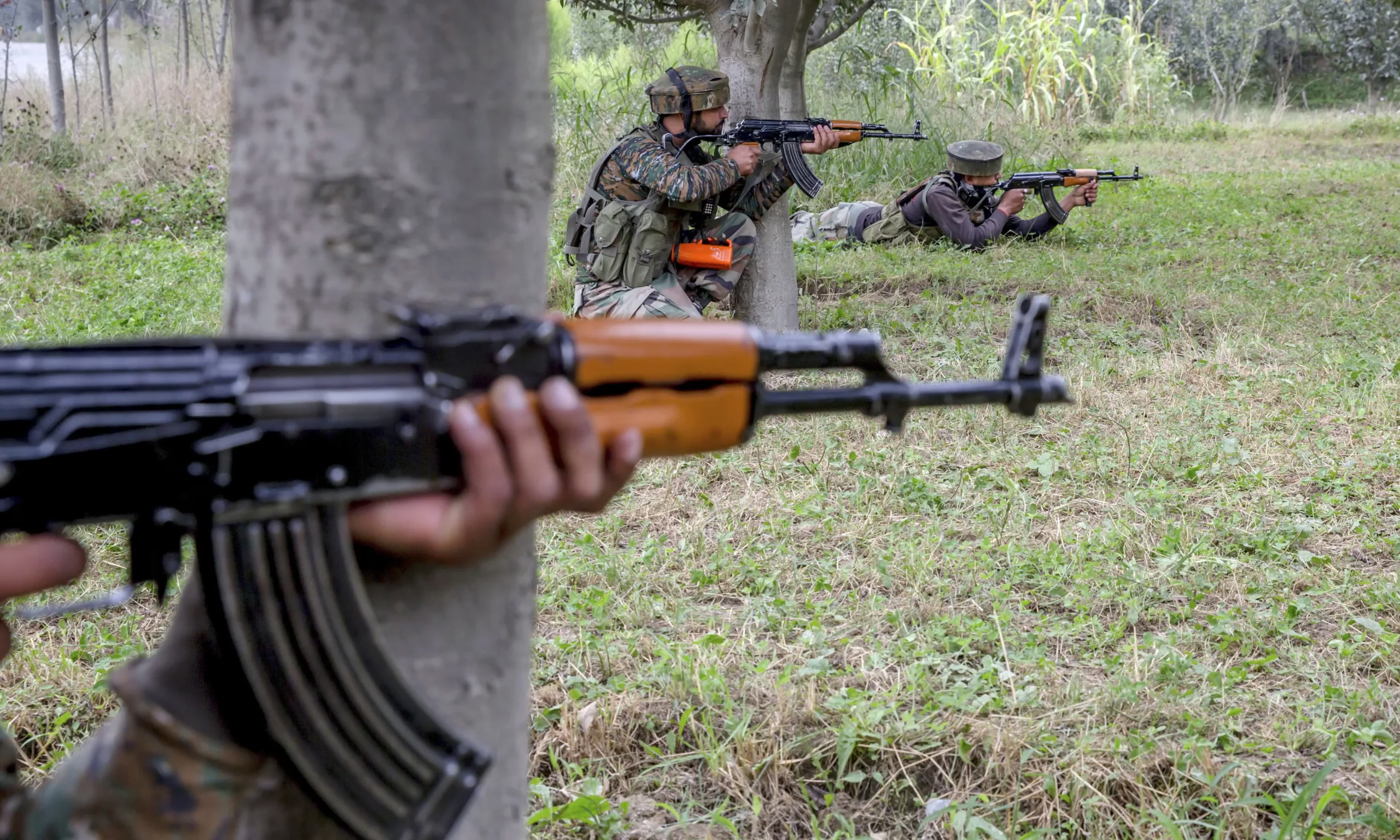
Among them is Yunus, who said his riverine homeland had been smashed by six punishing floods—”each one worse than the previous”—in the short time since he took over.
Hundreds of thousands of people were forced into emergency shelters in the floods, which also destroyed rice crops.
Also See: COP29 in Baku: The Make-or-Break Moment for Climate Action
‘You figure it out’
Bangladesh is among the world’s most vulnerable nations to climate change, with large areas made up of deltas where the Ganges and the Brahmaputra rivers wind towards the sea.
The country of 170 million is particularly at risk of devastating floods and cyclones—disasters that only stand to accelerate as the planet keeps warming.
Yunus said it was “not a secret” that rich nations would have to help poorer ones adapt and they should “figure out how much is needed—not me”.
“This is not something we are demanding out of your generosity. We’re asking because you are the cause of this problem,” he said bluntly.
Yunus said juggling a peaceful democratic transition and a floods response was “difficult” enough and adding a flight to Baku to feud over climate finance didn’t help.
Impatience for elections in Bangladesh has gained pace since Hasina’s ouster, and the silver-haired technocrat said he shared concerns for peace and security in the nation of 170 million.
A free and fair vote would come as promised, he said, but the speed of democratic reforms “will decide how quick the election will be”.
He wouldn’t offer a date or timeline, but said the caretaker administration was hoping to build “a quick consensus”.
“We are the interim government, so our period should be as short as possible,” he said.
This news is sourced from Fortune and is intended for informational purposes only.

![Muhammad Yunus criticizes COP29 talks as a "fish market," where poor nations beg for climate finance to address global issues. [Image via Fortune]](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/GettyImages-2184491912.webp)
![Ukrainian and Russian flags with soldier silhouettes representing ongoing conflict. [Image via Atlantic Council].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/2022-02-09T000000Z_1319661209_MT1NURPHO000HXCNME_RTRMADP_3_UKRAINE-CONFLICT-STOCK-PICTURES-scaled-e1661353077377.jpg)


![Truck traveling along the Makran Coastal Highway in Balochistan, with rugged cliffs and the Arabian Sea coastline in the background [Image via Getty Images].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Balochistan-2.webp)