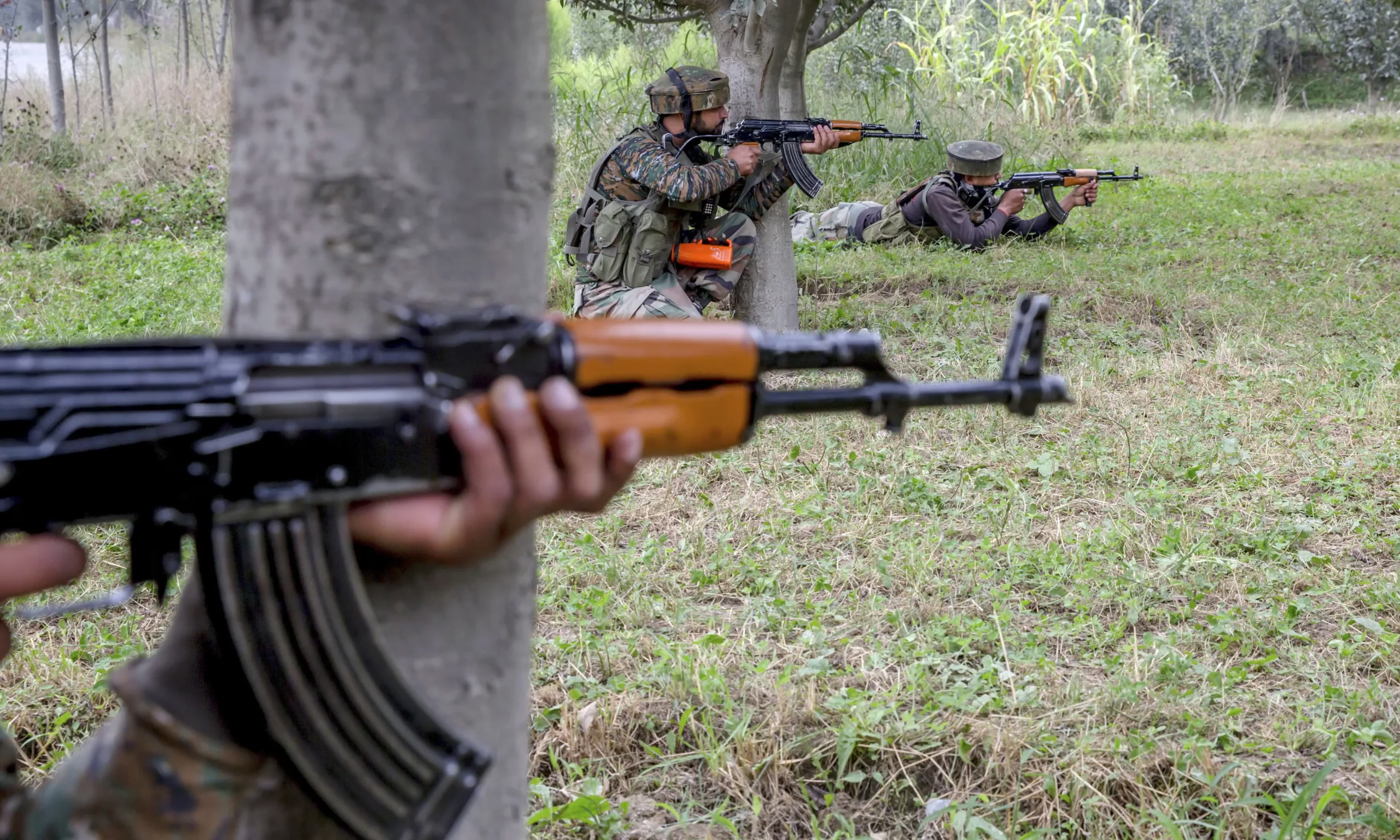
Pakistan is facing a growing risk of drought, following a significant reduction in rainfall across the country, with a 40% decrease in precipitation.
The 40% rainfall deficit in Pakistan has raised concerns about the increasing risk of drought, especially in areas where water resources are heavily dependent on seasonal rainfall.
According to the Meteorological Department, rainfall has been 40% lower than usual over the last four months, with varying degrees of shortage recorded across provinces, Express News reported.
The period from 1st September to 15th January saw a 52% drop in Sindh, while Balochistan experienced a 45% decrease. The Meteorological Department recorded a 42% shortfall in Punjab.
This rainfall deficit is also likely to bring forward the summer season, with rising temperatures expected in the coming days.
In several areas of Punjab, such as Pothohar, Layyah, Bhakkar, and Multan, light drought conditions have already begun to emerge. The Meteorological Department expects these conditions to worsen, particularly in rain-dependent areas.
The Meteorological Department has noted similar signs of drought in other regions, including Rajanpur, Bahawalpur, and Sargodha. Major cities such as Karachi, Hyderabad, and Badin in Sindh, as well as various towns in Balochistan, are also experiencing early-stage drought conditions.
The Meteorological Department has warned that if the current trend of low rainfall continues, the situation could deteriorate further. This would exacerbate the risk of widespread drought and heatwaves in the near future.
Also See: Punjab Muslims Pray for Rain Amid Smog Emergency
Cold and Dry Weather Expected
The Meteorological Department has forecasted cold and dry weather across most regions of Pakistan. Light rain and snowfall are expected in select northern areas.
According to the Meteorological Department, the weather will remain chilly and dry in the majority of the country. Cloud cover is expected in some places.
Regions such as Kashmir, Gilgit-Baltistan, and parts of northern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KPK) will see rain and snow in the coming days.
The Meteorological Department expects light snowfall in the higher mountain regions, including Chitral, Dir, Swat, Shangla, Kohistan, Mansehra, Battagram, Abbottabad, and Waziristan.
In Punjab, the weather will remain cold and dry, with no significant rainfall expected. Similarly, areas in Sindh are likely to experience cold and dry conditions.
In Balochistan, most districts will experience cold weather with some cloud cover. Light rain and snow are possible in the higher altitudes, including Quetta, Ziarat, Chaman, Pishin, Qila Abdullah, Barkhan, and Chagai.
Islamabad and its surrounding areas will experience cold weather, with the possibility of partly cloudy skies. The Meteorological Department expects intermittent rain and snowfall to overcast the northern regions of the country, including Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan.
This news is sourced from The Express Tribune and is intended for informational purposes only.

![Pakistan faces a growing risk of drought with a 40% rainfall deficit, threatening water resources and worsening drought conditions. [Image via Reuters]](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/La-Vinuela-reservoir-heatwave1717608772-0.webp)

![Ukrainian and Russian flags with soldier silhouettes representing ongoing conflict. [Image via Atlantic Council].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/2022-02-09T000000Z_1319661209_MT1NURPHO000HXCNME_RTRMADP_3_UKRAINE-CONFLICT-STOCK-PICTURES-scaled-e1661353077377.jpg)