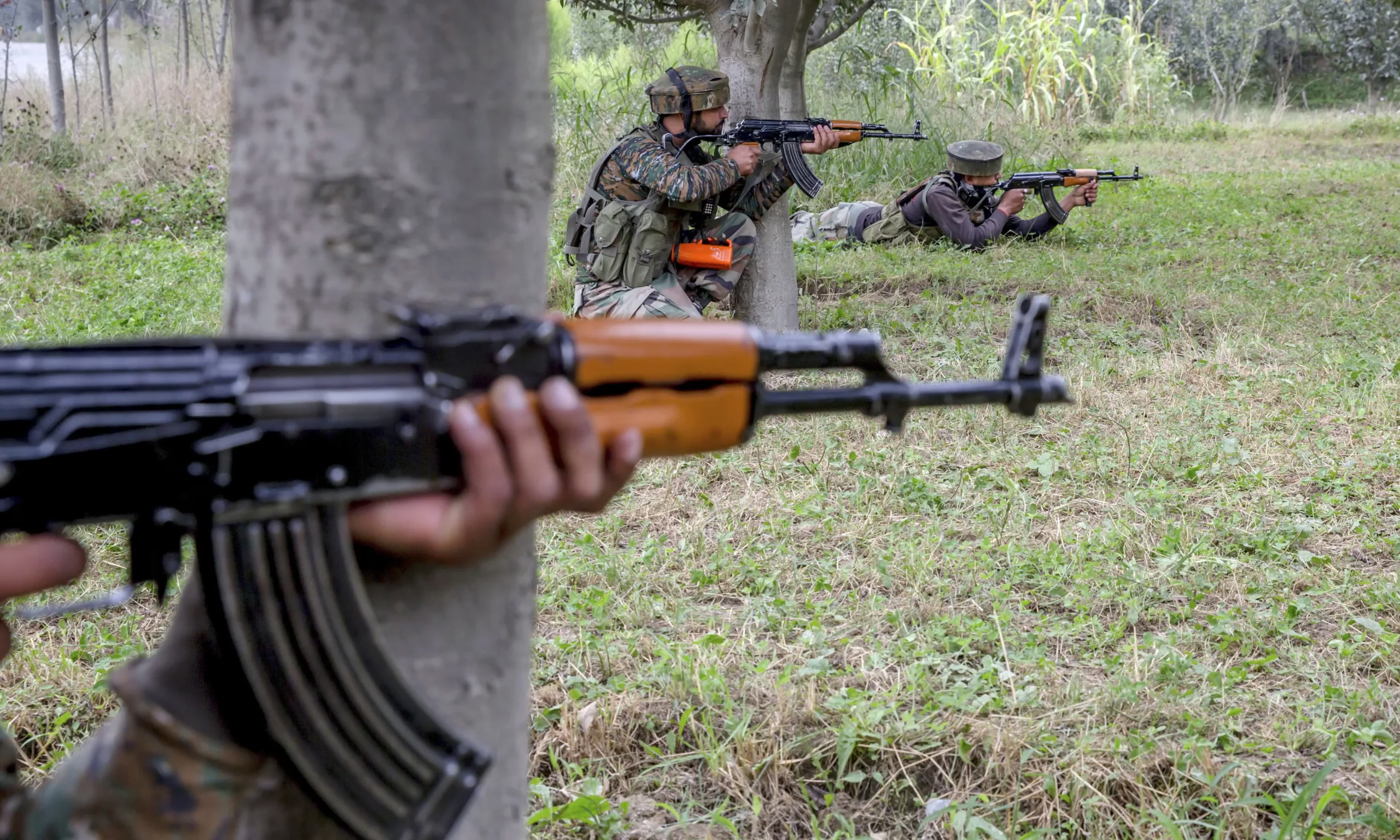
The Taliban administration in Afghanistan has conditionally agreed to allow Afghan women to pursue higher education in Pakistan. This agreement hinges on the condition that their male guardians, or mahrams, are granted visas to accompany them.
The announcement coincided with entrance exams held on Saturday, where hundreds of Afghan students competed for spots in graduate, postgraduate, and doctoral programs at Pakistani universities. Afghan refugees residing in Pakistan attended the tests in Peshawar and Quetta, while students within Afghanistan are scheduled to take the exams online in the coming days.
Pakistan’s special envoy for Afghanistan, Mohammad Sadiq, revealed that approximately 21,000 Afghan students, including over 5,000 women, had applied for the upcoming academic sessions under the fully funded Allama Iqbal Scholarship program. The Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan is tasked with selecting up to 2,000 Afghan students, with one-third of the spots reserved for female candidates.
An official from the Pakistani government, speaking on condition of anonymity, confirmed the Taliban’s conditional agreement and Pakistan’s commitment to issuing visas for guardians to ensure compliance with Afghan laws. The Taliban, however, have not officially commented on this development.
Also See: Afghanistan’s Taliban: Stuck in the Past, While the World Moves Forward
The scholarship initiative, designed to strengthen ties between the two nations, focuses on providing education in fields such as medicine, engineering, agriculture, and computer science. It had previously been disrupted after the Taliban regained power in 2021, banning girls’ education beyond the sixth grade and restricting Afghan women from traveling without male companions.
This recent decision marks a significant shift amid mounting criticism of the Taliban’s restrictions on women’s rights, which the United Nations has described as “gender apartheid.” While the Taliban defend their policies as compliant with Islamic law and Afghan culture, international calls for policy reversals persist.
The entrance exams come at a time of strained relations between Pakistan and Afghanistan, exacerbated by accusations that the Taliban harbor anti-Pakistan militants. Despite these tensions, both nations are working to foster cooperation in education, trade, and other sectors, with the hope of improving bilateral relations.
This news is sourced from The Express Tribune and is intended for informational purposes only.

![Afghan women to pursue education in Pakistan with Taliban's conditional approval; scholarships to boost bilateral ties. [Image via AFP]](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/afghan-student-pak1737987362-0.webp)
![Ukrainian and Russian flags with soldier silhouettes representing ongoing conflict. [Image via Atlantic Council].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/2022-02-09T000000Z_1319661209_MT1NURPHO000HXCNME_RTRMADP_3_UKRAINE-CONFLICT-STOCK-PICTURES-scaled-e1661353077377.jpg)


![Truck traveling along the Makran Coastal Highway in Balochistan, with rugged cliffs and the Arabian Sea coastline in the background [Image via Getty Images].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Balochistan-2.webp)