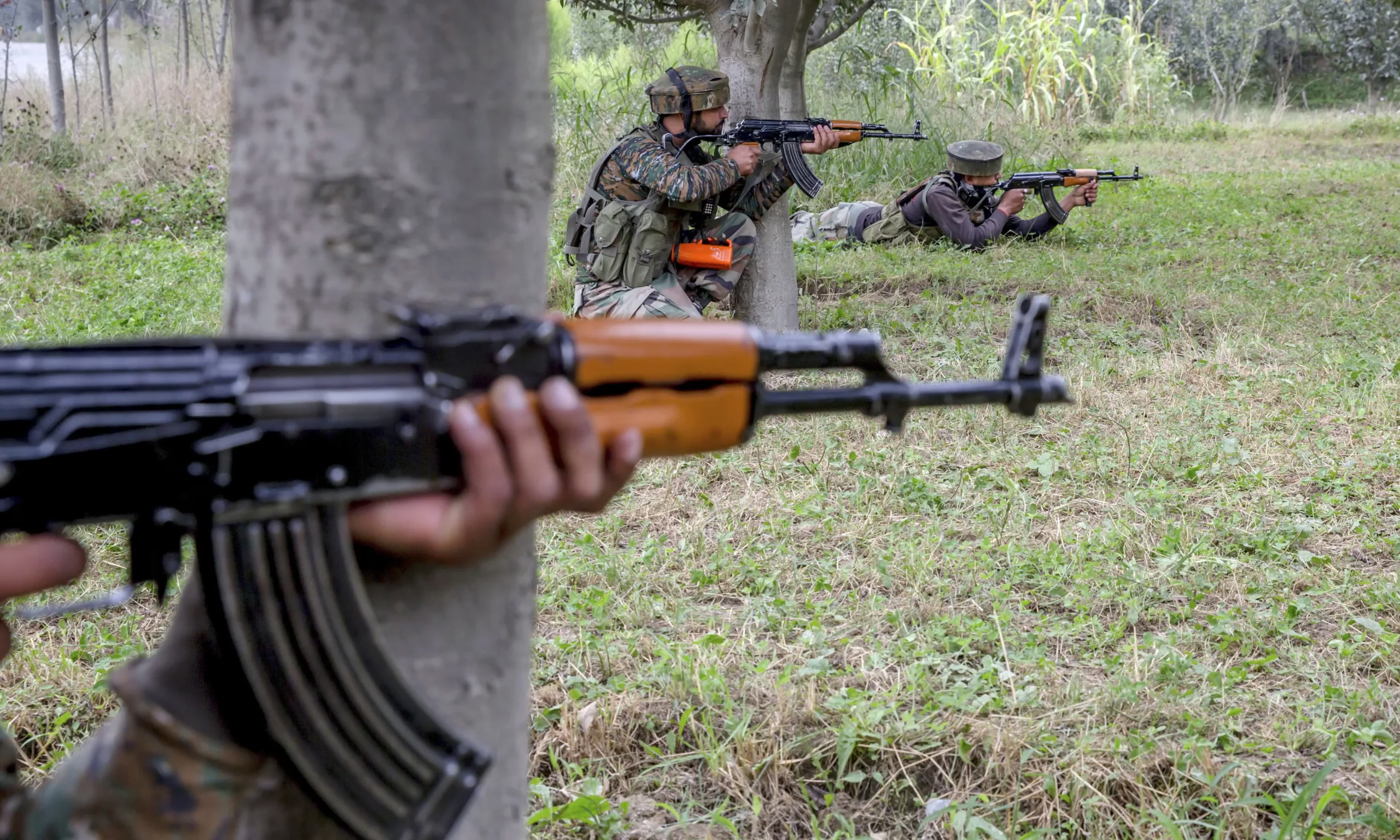
By 2030, Coca-Cola products will account for an estimated 602m kilograms of plastic waste entering the world’s oceans and waterways each year, according to a stark new analysis published Wednesday by the non-profit Oceana.
That is enough plastic to fill the stomachs of 18m whales.
The report arrives amid mounting concerns over the human health risks posed by the spread of microplastics, which scientists increasingly link to cancer, infertility and heart disease.
“Coca-Cola is by far the largest manufacturer and seller of beverages in the world,” said Matt Littlejohn, who leads Oceana’s campaigns targeting corporate polluters.
“Because of that, they really matter when it comes to the impact of all this on the ocean.”
Coca-Cola ranks as the world’s top branded plastic polluter, followed by PepsiCo, Nestlé, Danone and Altria, according to a 2024 study published in Science Advances.
Oceana’s estimate is based on Coca-Cola’s publicly reported packaging data from 2018 to 2023, combined with sales growth forecasts to create a “business-as-usual” scenario.
The result: the company’s plastic use is projected to exceed 4.13m tons annually by 2030.
To estimate how much of that plastic will reach aquatic ecosystems, researchers applied a peer-reviewed method developed by an international team of scientists and published in the academic journal Science in 2020 to arrive at the 602m kg estimate, which is equivalent to nearly 220bn half-litre bottles.
For Oceana, the clearest solution to reduce this staggering figure lies in bringing back reusable packaging – whether in the form of returnable glass bottles, which can be reused 50 times, or thicker PET plastic containers, which are designed for 25 uses.
Coca-Cola itself acknowledged in 2022 that reusable packaging was “among the most effective ways to reduce waste” and committed to a goal of reaching 25% packaging by 2030.
But that pledge was quietly dropped in its latest sustainability roadmap, released in December 2024.
The company’s updated goals instead focus on increasing recycled content in packaging and boosting collection rates – while stressing the significant challenges in recycling soda bottles and shifting consumer habits.
Environmental advocates have long warned against over-reliance on recycling, arguing that it often serves to shift blame on to consumers rather than addressing the root of the crisis.
“Recycling is great, don’t get me wrong,” Littlejohn said. “But if you’re going to use recycled plastic to produce more single-use plastic, that’s a problem.”
Also See: The Economics of Climate Change: Who Pays the Price?
Plastic production relies on oil, making corporate plastic use a direct driver of climate change.
Still, there is reason for hope: Coca-Cola already operates large-scale refillable systems in several countries, including Brazil, Germany, Nigeria and even parts of the United States, such as southern Texas.
“They have the largest reusable infrastructure of any beverage company and they have the ability to grow that and show the way for the rest of the industry,” Littlejohn said.
In a statement to AFP, a Coca-Cola spokesperson said that while the company’s efforts currently focus on using more recycled materials and improving collection systems, “we have been investing and remain committed to expand our refillable packaging options, and this work will continue as part of our consumer-centric strategy”.
This news is sourced from The Guardian and is intended for informational purposes only.

![Coca-Cola's plastic waste may hit 602m kg yearly by 2030. Oceana urges a shift to reusable packaging to cut pollution. [Photograph: Maria Mendiola/Surfers Against Sewage/PA]](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/35001.webp)
![Ukrainian and Russian flags with soldier silhouettes representing ongoing conflict. [Image via Atlantic Council].](https://southasiatimes.org/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/2022-02-09T000000Z_1319661209_MT1NURPHO000HXCNME_RTRMADP_3_UKRAINE-CONFLICT-STOCK-PICTURES-scaled-e1661353077377.jpg)